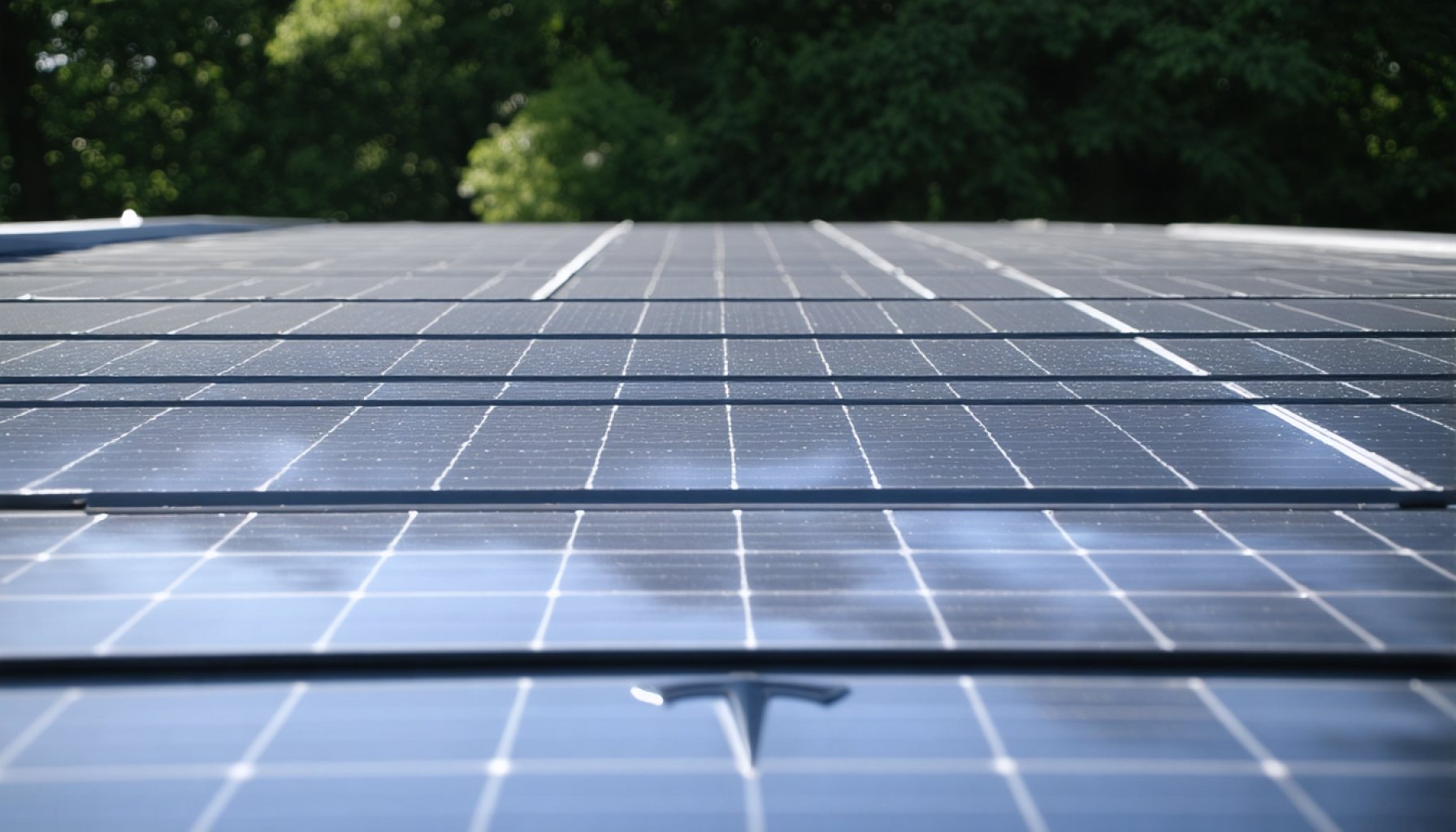
- Tesla’s Solar Roof tiles were introduced in 2016 as an innovative approach to integrate clean energy generation into building architecture.
- Initial goals to produce 1,000 solar roofs per week by 2019 faced setbacks, reaching far lower production levels by 2022 with only 23 installations per week.
- Tesla shifted its strategy from direct installations to partnering with third-party certified installers, focusing the company’s energy efforts elsewhere.
- The Solar Roof remains a premium product, with higher costs compared to traditional solar panels, limiting its accessibility and adoption.
- Despite limited deployment, the Solar Roof remains a part of Tesla’s energy offerings alongside more prevalent products like Megapacks and Powerwalls.
- The case of Tesla’s Solar Roof underscores the importance of balancing innovation with affordability and practicality for widespread success.
- Traditional solar panels continue to gain traction due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness, serving as the primary choice for homeowners seeking sustainable energy solutions.
When Elon Musk unveiled Tesla’s Solar Roof tiles in 2016, it felt like a glimpse into the future. A seamless marriage of energy and architecture, these innovative tiles promised to usher in an era where every rooftop could generate clean energy discreetly and elegantly. However, this vision hasn’t materialized as Musk once painted it.
Tesla set ambitious goals, aiming to produce 1,000 solar roofs per week by the close of 2019. Yet, dreams sometimes falter against the realities of production setbacks and market demands. It wasn’t until 2020 that the company finally reached a level of production, albeit still falling far short of its initial targets. By 2022, Tesla had managed to deploy just 2.5 MW of solar roofing, translating to about 23 installations per week—far from the envisioned scale.
The current landscape sees Tesla’s Solar Roof tiles shifting from its original pioneering stance to a more reserved role in the company’s portfolio. The company has pivoted its focus away from direct installations, handing over the reins to a network of third-party certified installers. Rather than Tesla’s grand rollout, prospective customers now seek quotes from these independent installers.
Financially, the Solar Roof remains a luxury rather than a mainstream solution. Its pricing skews towards the premium end of the market spectrum, making traditional solar panels coupled with durable roofing a more feasible option for many. This ineffable gap between aspiration and affordability might well be contributing to Tesla’s silence on recent deployment figures.
Despite its muted presence, the Solar Roof isn’t obsolete. Small-scale installations persist here and there, as seen recently in Topeka, Kansas. Yet, these instances are exceptions rather than the rule, amid an energy business now dominated by Tesla’s Megapacks and Powerwalls.
The fading prominence of the Solar Roof raises a crucial takeaway: while innovation is vital, ensuring accessibility and practicality equally defines a product’s success. Tesla’s experience reveals that transforming homes into clean energy powerhouses isn’t solely about sophisticated technology but also about meeting consumer needs on the ground.
As solar energy continues to advance, it’s clear that traditional solar panels are becoming the go-to solution for most homeowners. The simplicity, cost-effectiveness, and well-established nature of regular solar panels provide tangible steps toward sustainability today, even as the hopeful dream of converting every roof into a power generator continues to flicker on the horizon.
Tesla Solar Roof: A Dream Deferred or a Glimpse of What’s Next?
Introduction
Elon Musk’s 2016 unveiling of Tesla’s Solar Roof tiles painted a futuristic vision where architecture seamlessly integrated with clean energy generation. Yet, as of 2023, this vision remains unrealized. The ambitious rollout faced setbacks, and the Solar Roof’s current status reflects both challenges and evolution within Tesla’s energy strategy. This article delves into additional facts, potential real-world applications, and a balanced perspective on the current state of Tesla’s Solar Roof.
Production Challenges and Market Realities
1. Setbacks and Scale:
Tesla initially set a goal to produce 1,000 solar roofs per week by the end of 2019. Instead, production only moderated by 2020 and remained below expected levels, with just 23 installations per week by 2022.
2. Transition to Third-Party Installers:
Recognizing the logistical hurdles, Tesla shifted its focus from direct installations to a network of certified third-party installers, streamlining its operational focus on its more prominent energy products like Megapacks and Powerwalls.
3. Financial Viability:
The pricing of Solar Roof tiles remains a significant factor inhibiting mass adoption. Positioned as a premium product, they are often cost-prohibitive compared to traditional solar panels paired with durable roofing.
Real-World Applications and Insights
1. Limited Deployments:
Small-scale installations continue sporadically, as exemplified by recent installations in smaller towns like Topeka, Kansas. These cases reveal a persistent, albeit niche, interest in the Solar Roof.
2. Market Alternatives:
The robust market for traditional solar panels highlights their advantages: cost-effectiveness, quicker installations, and broader consumer acceptance, making them the favored choice for many homeowners.
Industry Trends and Future Outlook
1. Increasing Competition:
As other companies enter the solar roofing space, Tesla must innovate further or risk losing market relevance. Companies offering affordable and easy-to-install solar solutions are gaining traction.
2. Technological Advances:
The solar industry is experiencing rapid technological advancements. Innovators are exploring new materials and integration methods, which could see Tesla’s initial vision of widespread solar roofs eventually realized but perhaps by other market players.
3. Sustainability and Accessibility:
The importance of aligning innovative products with consumer affordability and accessibility is a lesson from Tesla’s Solar Roof journey. Future products must consider these elements to achieve widespread adoption.
Pros and Cons Overview
Pros:
– Aesthetically integrates with home architecture.
– Combines two functionalities: roofing and solar energy generation.
– Long-term energy savings potential.
Cons:
– High upfront costs limit accessibility.
– Production and deployment pace is slower than traditional solar options.
– Requires specific expertise for installation and maintenance.
Actionable Recommendations
For Homeowners Considering Solar:
– Evaluate Needs: Consider your energy consumption and potential savings before deciding on a solar investment.
– Financial Check: Review the financial impact, including installation costs and possible incentives or rebates.
– Compare Options: Research and receive quotes from both traditional solar panel providers and Solar Roof installers to determine the best fit for your situation.
– Seek Advice: Consult with energy experts or financial advisors to understand the long-term benefits and commitments.
Conclusion
While Tesla’s Solar Roof has not reshaped the clean energy landscape as anticipated, it remains a symbol of innovation that’s pushing the conversation forward. As we await further developments in solar technology, homeowners have a range of established, reliable solar solutions to choose from, allowing them to make meaningful strides toward sustainability today.
For more information on sustainable energy solutions, visit Tesla.